Do you want to know if you have heart damage from COVID-19? Call 470-735-5045
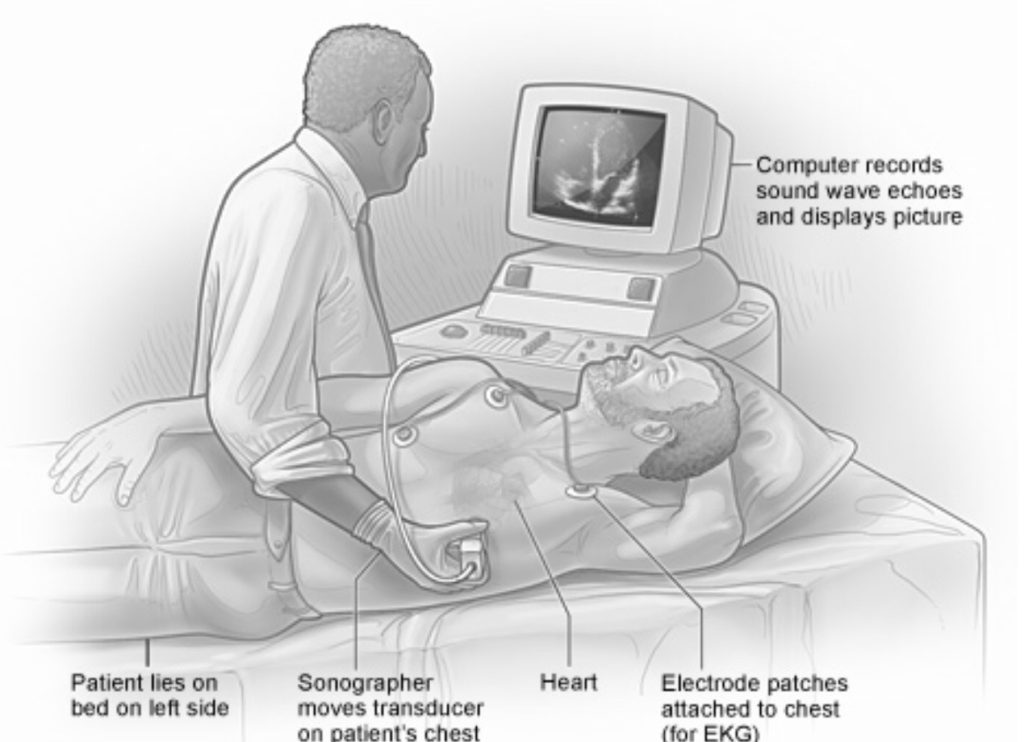
PREventClinic, Inc will help you find out if you have heart damage from a COVID-19 infection. In an easy and non-invasive, step-by-step process, we will evaluate your heart after COVID-19 infection. (Note: these diagnostics are intended for recovered patients (at least 3 weeks after the confirmed positive COVID-19 test to avoid spread.)
Persistent COVID-19 cardiac problems can hinder recovery for persons who have experienced COVID-19.
Some of the symptoms typical in coronavirus “long-haulers,” such as palpitations, dizziness, chest pain, and shortness of breath, could be caused by cardiac problems — or just from being infected with COVID-19. How can you identify if your symptoms are related to your heart, and what can you expect if they are?
Prevent Clinic cardiologists David E. Montgomery explain which post-coronavirus symptoms may indicate a cardiac problem, when to notify your doctor, and other information that all long-term COVID-19 survivors should be aware of.
Can COVID-19 cause heart damage?
Yes, although COVID-19 is largely a respiratory or lung condition, it can also affect the heart.
Several conditions might cause temporary or permanent cardiac tissue damage:
Lack of oxygen. Less oxygen can enter the circulation as the virus causes inflammation and fluid to fill the air sacs in the lungs. To pump blood through the body, the heart has to work harder, which can be harmful in patients who already have heart problems. Overworked hearts can fail, and insufficient oxygen can cause cell death and tissue damage in the heart and other organs.
Myocarditis: is a cardiac inflammation. As with other viral illnesses, including some types of the flu, the coronavirus may directly infect and damage heart muscle tissue. The heart may also be injured and inflamed indirectly as a result of the body’s immune system reaction.
Coronavirus infection also affects the inner walls of veins and arteries, causing inflammation, damage to extremely small capillaries, and blood clots, all of which can impair blood flow to the heart or other regions of the body. Severe COVID-19 is a disorder that damages the endothelial cells that line the blood arteries.
Cardiomyopathy caused by stress. Cardiomyopathy, a heart muscle illness that affects the heart’s ability to pump blood adequately, can be caused by viral infections. When the body is assaulted by a virus, it experiences stress and produces a surge of chemicals known as catecholamines, which can cause the heart to stop beating. When the infection is gone, the stressor is gone, and the heart may heal.